Description
 The American pika is a member of the Lagomorpha or rabbit family. It has a small, round body; peppery brown fur; large round ears, and no visible tail. It is between six and eight inches long and weighs about six ounces. The American pika is a member of the Lagomorpha or rabbit family. It has a small, round body; peppery brown fur; large round ears, and no visible tail. It is between six and eight inches long and weighs about six ounces.
Range 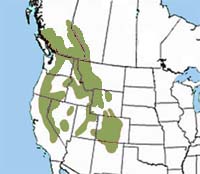 The American pika is found in the mountain areas of western North America from central British Columbia in Canada to Oregon, Washington, Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, Nevada, California and New Mexico. The American pika is found in the mountain areas of western North America from central British Columbia in Canada to Oregon, Washington, Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, Nevada, California and New Mexico.
Habitat
 The American pika lives in rocky mountain areas and boulder-covered hillsides, usually at elevations of between 8,000-13,000 feet. It makes its home in talus slopes (rock and boulder piles) at the base of cliffs. Although pikas live in groups, they are territorial and guard and defend their own area from other pikas. In the winter, the American pika stays in tunnels in the rock piles. The American pika lives in rocky mountain areas and boulder-covered hillsides, usually at elevations of between 8,000-13,000 feet. It makes its home in talus slopes (rock and boulder piles) at the base of cliffs. Although pikas live in groups, they are territorial and guard and defend their own area from other pikas. In the winter, the American pika stays in tunnels in the rock piles.
|
|
|
Diet
 The American pika is a plant-eater. It eats a variety of green plants like grasses, sedges, thistles, and fireweed. It eats some food on the spot, and it carries some food away to store in a pile or "haystack." The American pika is a plant-eater. It eats a variety of green plants like grasses, sedges, thistles, and fireweed. It eats some food on the spot, and it carries some food away to store in a pile or "haystack."
A pika haystack can contain as much as a bushel of plant matter! The pika often moves the pile to protect it from rain or to find a better drying spot. After the vegetation dries, the pika moves it to its den deep in the rocks. The pika is active all year. It eats food it has stored in the winter. If its supply runs low, it forages for lichen and cushion plants.
Life Cycle
The American pika first mates about one month before the snow starts to melt. Mating season typically runs from late April to early July. The female gives birth to two to four babies in the spring. The babies are weaned in about three to four weeks. The babies leave their mother after four weeks and are adult size in about three months. The female may then mate again and have a second litter.
The American pika has a lifespan of six to seven years in the wild.
Behavior
 The American pika is diurnal. Diurnal animals are active in the day. It spends most of the day sunning itself on the rocks; foraging for food; guarding its territory; or watching for predators like eagles, hawks, coyotes, bobcats, foxes, ermine, and weasels. The American pika is diurnal. Diurnal animals are active in the day. It spends most of the day sunning itself on the rocks; foraging for food; guarding its territory; or watching for predators like eagles, hawks, coyotes, bobcats, foxes, ermine, and weasels.
 The American pika is a very vocal animal! It uses both call and song vocalizations. The call is used to warn other pikas of a predator or intruder, and it sounds a little like the bleat of a goat. The song is used mostly by males during mating season, although females use the call in the fall. The American pika is a very vocal animal! It uses both call and song vocalizations. The call is used to warn other pikas of a predator or intruder, and it sounds a little like the bleat of a goat. The song is used mostly by males during mating season, although females use the call in the fall.
|



 The American pika is found in the mountain areas of western North America from central British Columbia in Canada to Oregon, Washington, Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, Nevada, California and New Mexico.
The American pika is found in the mountain areas of western North America from central British Columbia in Canada to Oregon, Washington, Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, Nevada, California and New Mexico.



